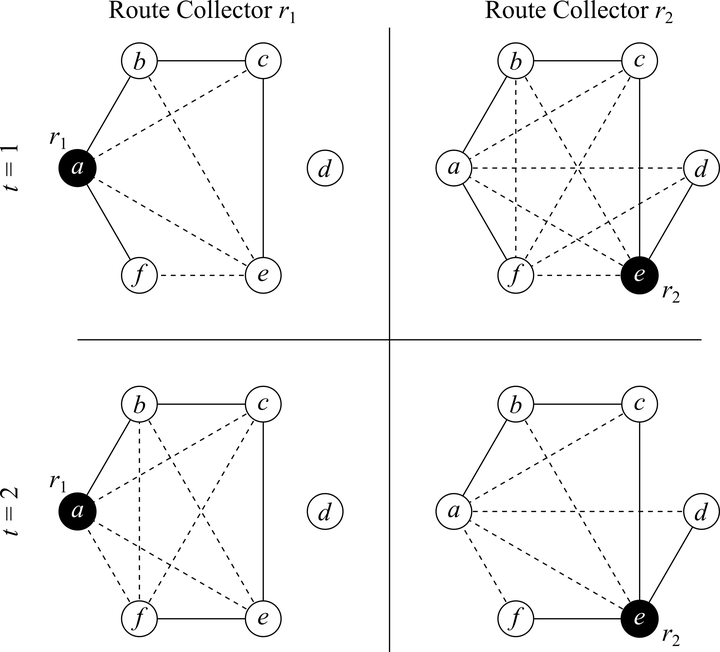
Abstract
The Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is a distributed protocol that manages interdomain routing without requiring a centralized record of which autonomous systems (ASes) connect to which others. Many methods have been devised to infer the AS topology from publicly available BGP data, but none provide a general way to handle the fact that the data are notoriously incomplete and subject to error. This paper describes a method for reliably inferring AS-level connectivity in the presence of measurement error using Bayesian statistical inference acting on BGP routing tables from multiple vantage points. We employ a novel approach for counting AS adjacency observations in the AS-PATH attribute data from public route collectors, along with a Bayesian algorithm to generate a statistical estimate of the AS-level network. Our approach also gives us a way to evaluate the accuracy of existing reconstruction methods and to identify advantageous locations for new route collectors or vantage points.